Author’s Note: My wife (who is a nurse practitioner) and I recently attended an event for leadership at a prominent health system. Several conversations reflected both the benefits and concerns of AI in the healthcare environment. This ambivalence suggested an even bigger question: Is the organization ready to generate responsible AI? These concerns led me to create this three-part series on ‘AI Readiness.’ —Chris
Trusted data must encompass eight attributes
So, what is trusted data? Trusted data refers to information that is reliable, accurate, secure, and compliant with relevant regulations and standards.
In the context of healthcare, trusted data specifically pertains to the data collected, stored, processed, and shared within the healthcare data ecosystem, to include all clinical, operational, and financial data available to a hospital or health system.
“There is a risk of data inputs being very selective in the information they feed to AI, manifesting a very narrow understanding of topics which are potentially more complicated. This problem is more than just a theoretical concern, as there have already been examples of AI arriving at incorrect conclusions because of the data received.”
International Bar Association, Nov. 2023
Key attributes of trusted data include:
- Accuracy: Trusted data is free from errors, inconsistencies, or inaccuracies. It reflects the most up-to-date and precise information.
- Security: Trusted data is protected against unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, or destruction.
- Privacy: Trusted data upholds patient privacy by ensuring that personally identifiable information and sensitive healthcare information are handled securely and in compliance with relevant privacy regulations.
- Compliance: Trusted data adheres to applicable regulations, standards, and industry best practices governing the collection, storage, processing, and sharing of healthcare information.
- Interoperability: Trusted data is interoperable, meaning it can be exchanged, integrated, and accessed seamlessly across different healthcare systems, organizations, and platforms.
- Transparency: Trusted data is transparently managed and documented, with clear accountability, audit trails, and governance mechanisms.
- Consent and ethics: Trusted data respects patient autonomy and ethical principles by obtaining informed consent for data collection, use, and sharing.
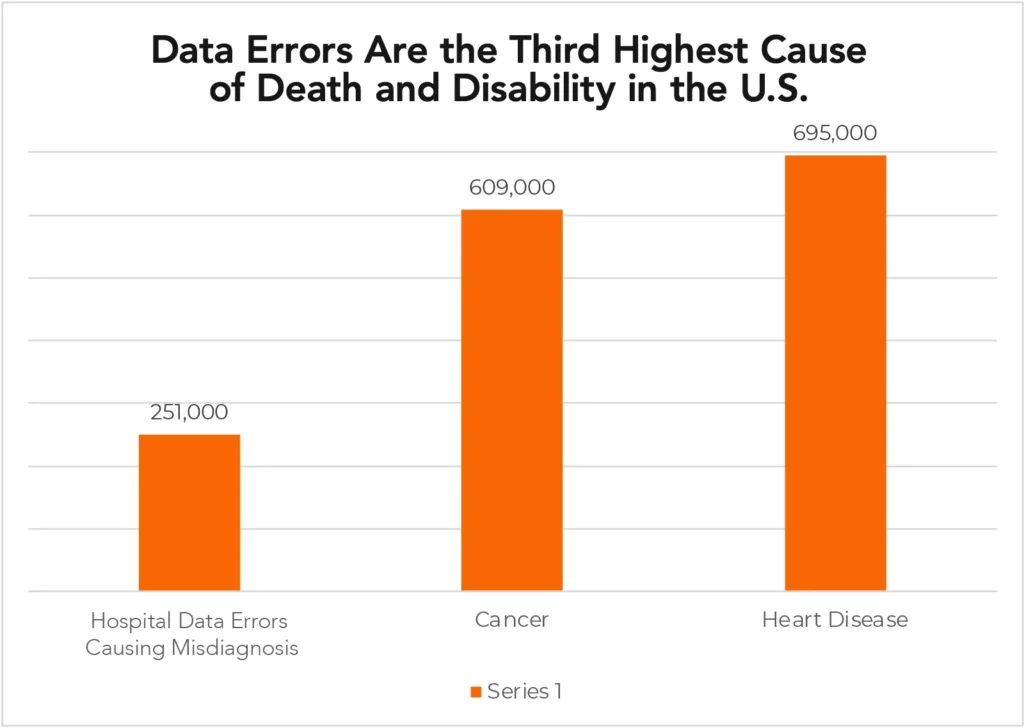
Source: Association of Health Care Journalists, 2023.
The absence of any of these key attributes will compromise any AI-driven solution or outcome.

